UK Environmental Accounts: 2023
6th June 2023
Measuring the contribution of the environment to the economy, impact of economic activity on the environment, and response to environmental issues.
UK greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions on a residence basis increased by 3% to just over 502 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (Mt Co2e) between 2020 and 2021.
The impact of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic on emissions would likely have been weaker than in 2020 because of fewer UK pandemic restrictions in 2021.
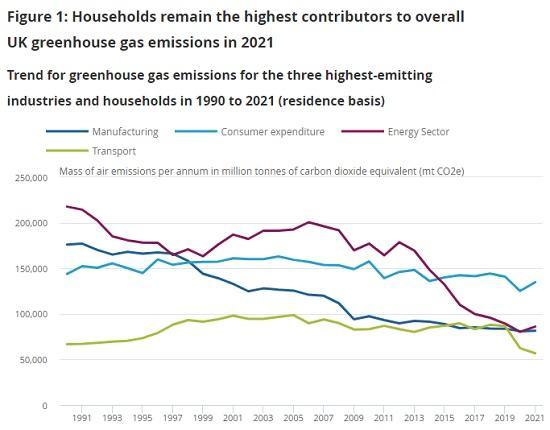
Consumer expenditure is still the largest single UK emissions contributor, at 26% of the 2021 total; the energy sector was second highest at 17%.
Energy from renewable sources accounted for 13% of total UK energy use in 2021, decreasing slightly from 14% in 2020.
Output from the UK environmental goods and services sector (EGSS) was estimated to be £89.6 billion in 2020, up 1.4% from 2019.
Employment in the UK EGSS was estimated to be 398,800 full-time equivalent employees in 2020, up 2.2% from 2019.
Greenhouse gas emissions
Total UK greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions (residence basis) in 2021 were just over 502 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent (Mt Co2e). Information about the different method used to measure emissions can be found in the Measuring UK greenhouse gas emissions article, available on the UK climate change statistics Portal.
The transport sector's emissions reduced by 9% in 2021 following a 28% fall in 2020; the largest decrease (34%) of all sectors since 2019.
Emissions from households, accounted for through consumer expenditure, are the largest single contributor to UK emissions. In 2021, emissions related to consumer expenditure - primarily from heating homes and travelling - rose 7% to 135 Mt Co2e in 2021, 26% of the total. The second highest emitter was the energy sector, rising 7% to reach 86 Mt Co2e, 17% of the total.
Greenhouse gas emission intensity
A reduction in overall UK greenhouse gas (GHG) emission intensity would, in theory, indicate that the UK is moving towards a lower carbon economy.
In 2021, the UK emitted 0.19 thousand tonnes of Co2e per £ million of gross value added (GVA). This is a drop of 67% since 1990.
Agriculture, forestry and fishing was by far the most emission intensive industry in 2021 after surpassing electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning supply in 2016. This is likely a combination of the agriculture industry being the heaviest emitter of the potent GHG CH4 (Methane) and the reduction in emission intensity from the electricity industry.
Energy use
Most greenhouse gas emissions are related to energy use. The UK used a total of almost 176 million tonnes of oil equivalent (Mtoe) of energy in 2021, with 80% coming from fossil fuels.
In 2021, energy from renewable sources accounted for 13% of all energy use in the UK, compared with 0.9% in 1990. Energy use from fossil fuels has been falling for the energy and manufacturing sectors, largely because of a switch from the use of coal to other fuels, such as natural gas, which generate lower emissions.
Read the full report HERE