AI and Employee Absence 2026 - The New Watchdog of Workplace Wellbeing
1st January 2026
In modern workplaces, employee absence is more than a simple inconvenience -it can disrupt operations, inflate costs, and strain teams.
For decades, managers have relied on spreadsheets, HR reports, and intuition to understand sickness patterns, often reacting after the fact.
Now, artificial intelligence is beginning to change that dynamic, promising a proactive, data-driven approach to monitoring, analysing, and even predicting staff absences.
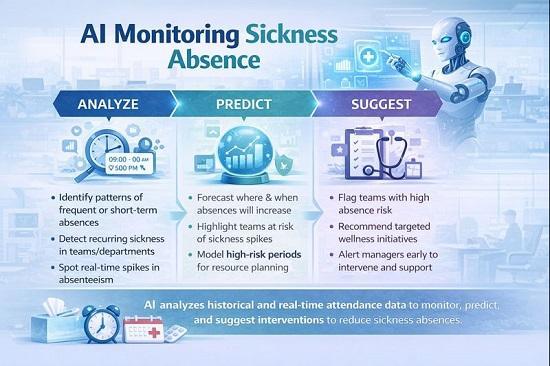
AI systems can process vast amounts of historical and real-time attendance data, detecting patterns invisible to the human eye.
Frequent short-term absences, recurring illness trends, or sudden spikes in absenteeism can be flagged immediately. Machine learning models go further, predicting where and when absences are most likely to occur.
These insights allow managers to plan staffing more effectively, schedule temporary cover in advance, and prevent service disruption. For high-pressure sectors such as healthcare or public services, this capability is particularly valuable, ensuring that critical operations remain functional even when illness strikes.
Beyond prediction, AI can support wellbeing initiatives. By integrating anonymized data on workload, overtime, and employee engagement, AI can identify departments or teams under strain, offering management the opportunity to intervene before absences escalate.
Suggested interventions may include adjustments to working hours, targeted health and wellness programs, or mental health support. In this sense, AI is not simply policing absence—it becomes a tool for promoting employee welfare while safeguarding organisational efficiency.
Private companies are increasingly adopting AI to optimise workforce planning, reduce overtime costs, and maintain productivity. In the public sector, similar systems are emerging in hospitals, local councils, and government agencies, where unplanned absences can directly affect public services. In both contexts, AI can act as an early-warning system, highlighting potential issues before they become crises and giving managers actionable intelligence to support staff effectively.
However, the adoption of AI in monitoring sickness absences is not without challenges. Privacy is paramount; employees' medical information and personal circumstances must be protected under legal frameworks such as data protection laws.
Over-reliance on AI or miscommunication about its purpose can undermine trust and morale, creating perceptions of surveillance or unfair judgment. AI can identify patterns, but it cannot fully comprehend context—legitimate health issues or personal crises still require human understanding and sensitivity.
Moreover, predictive models trained on historical data risk reinforcing biases, for instance penalizing staff in roles or departments with higher inherent stress levels.
Despite these challenges, the trajectory is clear. AI will increasingly shape how organisations understand and manage employee absence. It offers the promise of more responsive staffing, better support for employee wellbeing, and reduced operational disruption. But to succeed, AI must be integrated with careful policy design, transparent communication, and human oversight. It is not a replacement for management or compassion; it is a powerful tool that, when used responsibly, can transform the way organisations approach sickness, productivity, and staff welfare.
In the near future, absence management may no longer be reactive or anecdotal. Instead, AI will provide real-time insights, predictive alerts, and data-driven recommendations, ensuring that organisations can support their workforce while maintaining operational resilience.
In this emerging landscape, AI is poised to become both a guardian of productivity and an advocate for wellbeing - a silent but vigilant partner in the modern workplace.